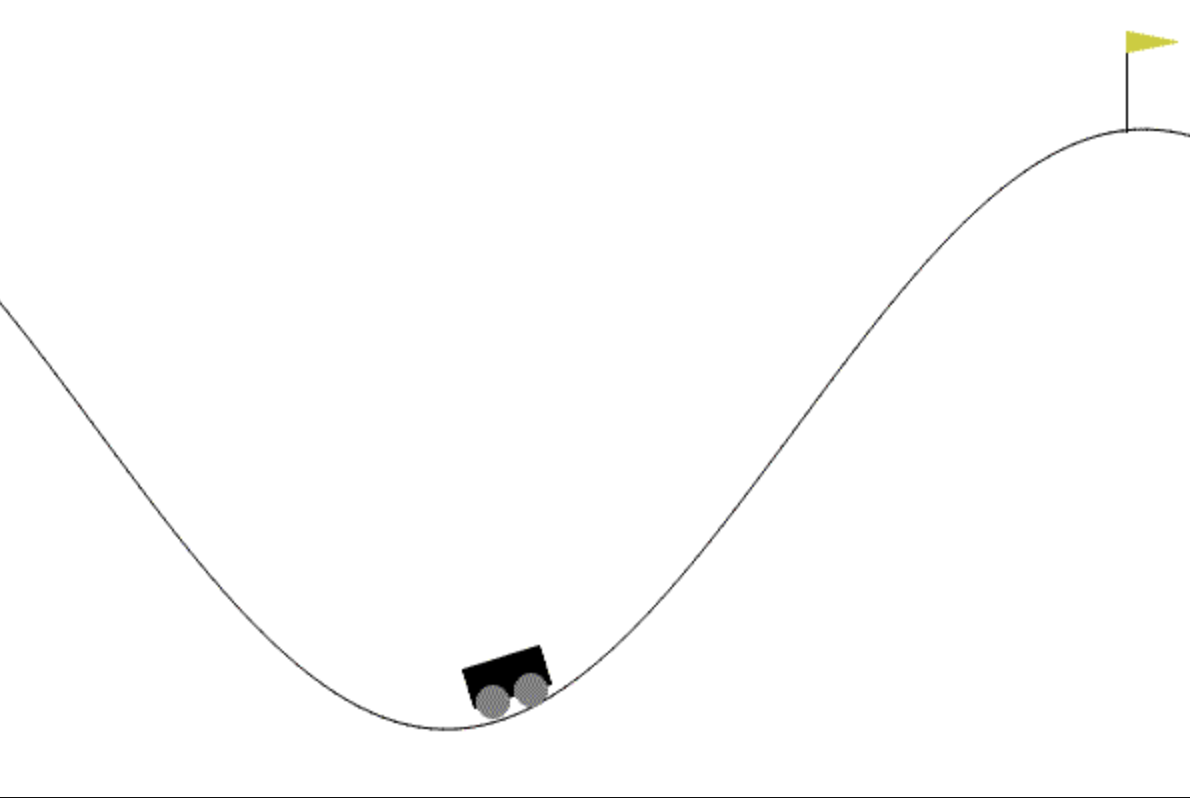
First you need to install two libraries for python with pip
pip install gym
pip install numpy
Now the Code for the the Game
# objective is to get the cart to the flag.
# for now, let's just move randomly:
import gym
import numpy as np
env = gym.make("MountainCar-v0")
LEARNING_RATE = 0.1
DISCOUNT = 0.95
EPISODES = 27000
SHOW_EVERY = 3000
reachCount = 0;
DISCRETE_OS_SIZE = [20, 20]
discrete_os_win_size = (env.observation_space.high - env.observation_space.low)/DISCRETE_OS_SIZE
# Exploration settings
epsilon = 1 # not a constant, qoing to be decayed
START_EPSILON_DECAYING = 1
END_EPSILON_DECAYING = EPISODES//2
epsilon_decay_value = epsilon/(END_EPSILON_DECAYING - START_EPSILON_DECAYING)
q_table = np.random.uniform(low=-2, high=0, size=(DISCRETE_OS_SIZE + [env.action_space.n]))
def get_discrete_state(state):
discrete_state = (state - env.observation_space.low)/discrete_os_win_size
return tuple(discrete_state.astype(np.int)) # we use this tuple to look up the 3 Q values for the available actions in the q-table
for episode in range(EPISODES):
discrete_state = get_discrete_state(env.reset())
done = False
if episode % SHOW_EVERY == 0:
render = True
reachCount = 0
print(episode)
else:
render = False
while not done:
if np.random.random() > epsilon:
# Get action from Q table
action = np.argmax(q_table[discrete_state])
else:
# Get random action
action = np.random.randint(0, env.action_space.n)
new_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
new_discrete_state = get_discrete_state(new_state)
if episode % SHOW_EVERY == 0:
env.render()
# If simulation did not end yet after last step - update Q table
if not done:
# Maximum possible Q value in next step (for new state)
max_future_q = np.max(q_table[new_discrete_state])
# Current Q value (for current state and performed action)
current_q = q_table[discrete_state + (action,)]
# And here's our equation for a new Q value for current state and action
new_q = (1 - LEARNING_RATE) * current_q + LEARNING_RATE * (reward + DISCOUNT * max_future_q)
# Update Q table with new Q value
q_table[discrete_state + (action,)] = new_q
# Simulation ended (for any reson) - if goal position is achived - update Q value with reward directly
elif new_state[0] >= env.goal_position:
#q_table[discrete_state + (action,)] = reward
reachCount += 1
print("Goal reached: ", reachCount)
q_table[discrete_state + (action,)] = 0
discrete_state = new_discrete_state
# Decaying is being done every episode if episode number is within decaying range
if END_EPSILON_DECAYING >= episode >= START_EPSILON_DECAYING:
epsilon -= epsilon_decay_value
env.close()
Now you can run the application. You should see the car which tries to climb the hill multiple Times. After a litte time for the ML to learn with the q-tables, the ML should understand how to climb the hill and make an easy ride up the hill.